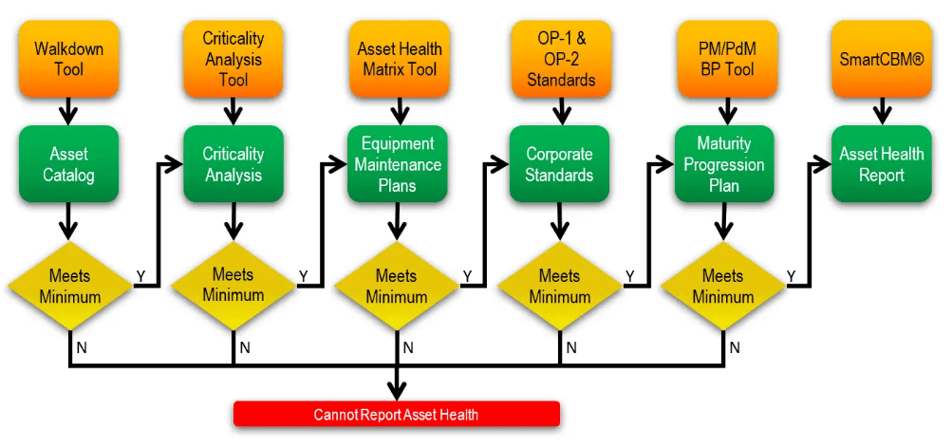
How Allied Reliability Can Help
Allied Reliability’s Equipment Health Assurance consulting offering begins by addressing two basic but critical questions: “How Much?” and “How Well?” How much refers to the percentage of the asset base being covered and the number of failure modes addressed on those assets. How well refers to the amount of rigor being applied to these standards across all facilities.
Allied Reliability works within your organization to focus on the early identification and elimination of defects. This early identification of the defects will then lead to consulting and coaching on facilitating proactive work. This is in marked contrast to utilizing technologies to optimize a run-to-failure maintenance strategy.
If you have an optimized preventive maintenance (PM) / condition monitoring process that is failure mode driven, that process (including inspections and follow-up work orders) drives 75-85% of your workflow. It considers various factors, ranging from manufacturer information and equipment history to real-time data such as vibration analysis. If you plan your maintenance schedule, execute the work with precision, and have a continuous improvement process, you will be a pacesetter and generate a positive impact to your bottom line.